
If the likelihood is remote, no disclosure is generally required unless required under another ASC topic. However, if a remote contingency is significant enough to potentially mislead financial statement users, the company may voluntarily disclose it. ROU assets are typically amortized on a straight-line basis over the lease term unless another method better reflects the pattern of use. This process allocates the cost of the ROU asset over its useful life.
What Is A Balance Sheet? Definition and Examples
- Other balance sheets are presented using the report-form method, which is the most common method of balance sheet presentation.
- When a business borrows money, the obligations to repay the principal amount, as well as any interest accrued, are recorded on the balance sheet as liabilities.
- An expense is the cost of operations that a company incurs to generate revenue.
- We use the long term debt ratio to figure out how much of your business is financed by long-term liabilities.
- Small businesses that aren’t required to comply with the US GAAP may opt not to consider contingencies in financial reporting.
- Equity is the value of all the assets a company holds minus any money owed.
Overall, liabilities will almost always require future payments depending on the agreement between you and the other party involved. At Alaan, we empower businesses to manage their expenses precisely and easily. Our AI-powered spend management platform provides real-time insights into Accounting For Architects vendor payments and operational costs, helping you maintain better control over cash flow and liabilities. These are short-term obligations that a business must settle within one year.

Adjustments for Lease Modifications
- These updates provide a clearer view of a company’s financial obligations and asset utilization, aiding stakeholders in assessing financial health and operational efficiency.
- Legal and financial advisors can provide insights into the likelihood of contingencies and help estimate potential losses.
- These taxes are typically reported on the company’s income statement and recognized as a liability on the balance sheet.
- Expenses are continuing payments for services or things of no financial value.
- Financial ratios involving liabilities provide insights into the liquidity, leverage, and overall financial stability of a business.
In financial accounting, a liability is a quantity of value that a financial entity owes. Also sometimes called “non-current liabilities,” these are any obligations, payables, loans and any other liabilities that are due more than 12 months from now. Contingent liabilities are potential future obligations that depend on the occurrence of a specific event or condition.
- Our AI-powered spend management platform provides real-time insights into vendor payments and operational costs, helping you maintain better control over cash flow and liabilities.
- A positive net worth indicates that a company has more assets than liabilities, while a negative net worth indicates that a company’s liabilities exceed its assets.
- However, if you know the characteristics of a liability, you can categorize a transaction as one.
- Your concise guide to understanding GnuCash’s role in financial software.
- Maybe it’s because you bought them a drink or did a favor for them.
- Liabilities are settled over time through the transfer of economic benefits including money, goods, or services.
Liabilities vs. Expenses
She has more than five years of experience working with non-profit organizations in a finance capacity. Keep up with Michelle’s CPA career — and ultramarathoning endeavors — on LinkedIn. Here are a few quick summaries to answer some of the frequently asked questions about liabilities in accounting. Assets are what are retained earnings broken out into current assets (those likely to be converted into cash within one year) and non-current assets (those that will provide economic benefits for one year or more).
How do I calculate my liability?

These liabilities may or may not materialize, and their outcome is often uncertain. Examples of contingent liabilities include warranty liabilities and lawsuit liabilities. A liability is generally an obligation between one party and another that’s not yet completed or paid. For modifications not accounted for as separate leases, the lease liability is recalculated to align with new terms.

Examples of Contingent Liabilities
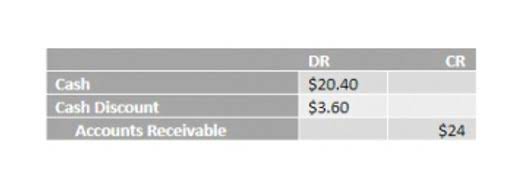
The AT&T example has a relatively high debt level under current liabilities. Other line items like accounts payable (AP) and various future liabilities like payroll taxes will be higher current debt obligations for smaller companies. It’s critical for business owners and managers to understand how to present contingent liabilities accurately in the financial statements. Under U.S. Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP), some contingent losses may be reported on the balance sheet and income statement, while others are only disclosed in the footnotes. Here’s an overview of the rules for properly identifying, measuring and reporting contingencies to provide a fair and complete picture of your company’s financial position.
- This ensures interest expenses are recognized over the lease term.
- Now, after understanding how to calculate liabilities, the next step is to explore the financial ratios that use these figures to evaluate a company’s debt management and overall economic health.
- However, if a remote contingency is significant enough to potentially mislead financial statement users, the company may voluntarily disclose it.
- This is often used as operating capital for day-to-day operations by a company of this size rather than funding larger items which would be better suited using long-term debt.
- It means that crediting liability accounts increases their balances while debiting them decreases their balances.
- An equitable obligation is a duty based on ethical or moral considerations.
Understanding Tenant Compensation for Inconvenience in Queensland: A Complete Guide
Hence, businesses are liable to pay salaries and wages to their employees after the employees have performed their duties. These features give businesses the insights needed to improve creditworthiness, stabilise operations, and make data-driven decisions. With liability accounts Alaan, managing liabilities becomes simpler, smarter, and more efficient. At Alaan, our Corporate Cards offer real-time visibility into team expenses, allowing you to streamline vendor payments and maintain better cash flow control. By using this method, businesses can calculate and cross-check their liabilities accurately, ensuring their financial statements remain consistent and reliable.

